Maximize Weight Loss: Harness the Power of Green Tea
Green tea, derived from the Camellia sinensis plant, has been celebrated for centuries in various cultures for its numerous health benefits, particularly in weight management and disease prevention. This in-depth exploration delves into the scientific underpinnings of green tea's health benefits, focusing on its chemical constituents, their interactions with the human body, and practical guidance for incorporating green tea into your wellness regimen.
The Bioactive Compounds of Green Tea
Green tea is rich in polyphenols, which are natural compounds that have health benefits, such as reducing inflammation and helping to fight cancer. Among the most potent of these is Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG), known for its powerful anti-oxidative properties. Besides EGCG, green tea contains other catechins such as epicatechin, epicatechin-3-gallate, and epigallocatechin, each contributing uniquely to its health-promoting properties.
- Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG): This is the most studied catechin in green tea. EGCG is effective in enhancing metabolic health by influencing various enzymes and hormones that modulate thermogenesis and fat oxidation.
- Epicatechin (EC): This antioxidant improves heart health by enhancing blood flow and reducing arterial stiffness.
- Epicatechin Gallate (ECG): Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, ECG plays a role in preventing chronic diseases related to inflammation.
- Epigallocatechin (EGC): It aids in the reduction of lipid levels in the blood and improves overall cardiovascular health.
Additionally, green tea contains amino acids like L-theanine, which promotes relaxation and enhances mood without the sedative effects found in many other calming substances.
How Green Tea Affects the Body
The health benefits of green tea are extensive, ranging from metabolic enhancement to improved heart health and beyond.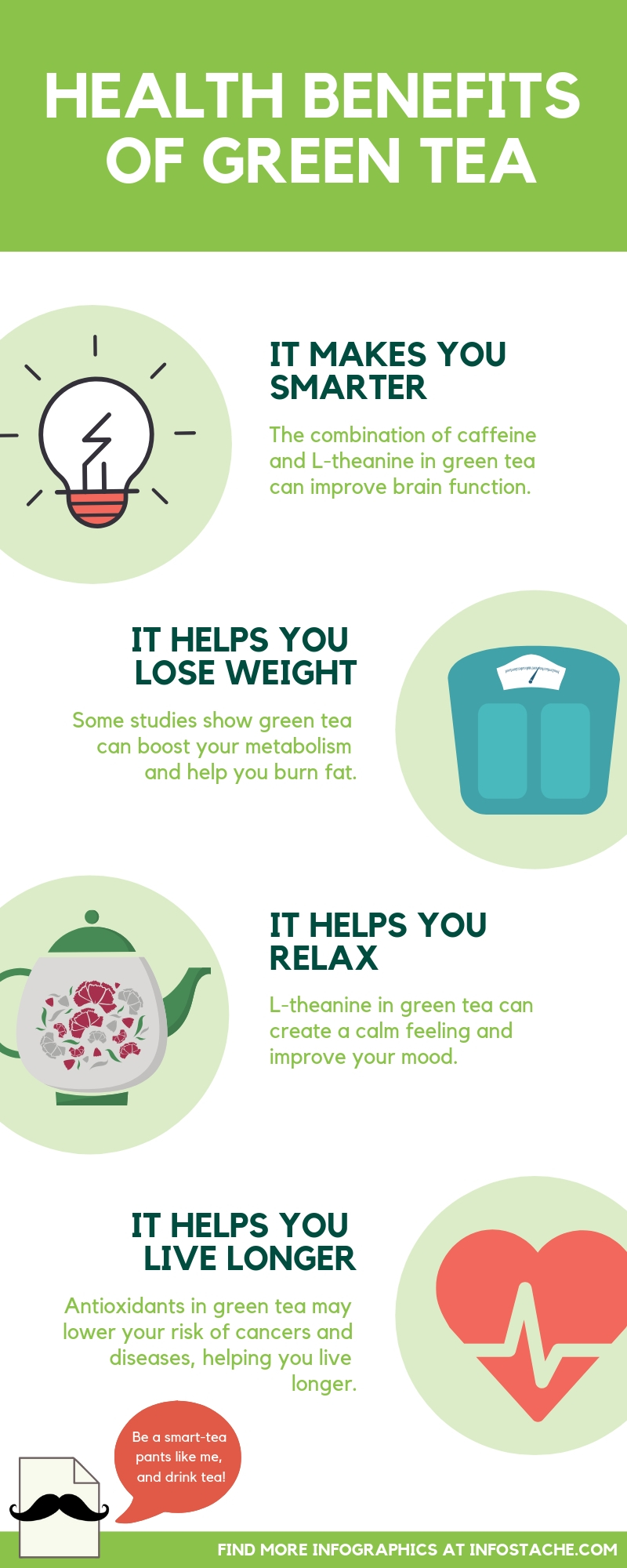
- Metabolic Rate Increase: EGCG is a natural antioxidant that significantly increases the body's metabolic rate. This catechin interacts with the nervous system to induce fat burning, specifically through the process of thermogenesis where the body burns calories to digest food and produce heat.
- Fat Oxidation: Green tea has been shown to enhance the rate at which your body turns food into calories, which is crucial for weight loss and weight management.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: The polyphenols and polysaccharides in green tea are effective in lowering blood sugar levels, thereby helping to manage diabetes symptoms.
- Enhanced Mental Alertness and Cognitive Function: The mild caffeine content of green tea can enhance brain function, resulting in improved mood, vigilance, reaction time, and memory.
- Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Effects: The high level of antioxidants in green tea helps combat oxidative stress and inflammation in the body, contributing to the prevention of chronic illnesses such as heart disease and cancer.
Incorporating Green Tea into Your Diet
Integrating green tea into your daily regimen can be done in several enjoyable and effective ways:
- Brewed Tea: Drinking 3-4 cups of green tea daily can significantly enhance your antioxidant intake.
- Green Tea Extracts: For those who prefer not to drink large amounts of tea, green tea extracts can provide a concentrated dose of polyphenols and catechins.
- Incorporation into Meals: Green tea powder can be added to smoothies, yogurts, and even used in cooking, providing a nutritional boost without significantly altering the taste of dishes.
FAQs About Green Tea and Weight Loss
How much green tea should I drink to lose weight?
To achieve weight loss benefits, it is recommended to drink 3-4 cups of green tea per day. This provides a sufficient dose of EGCG and other catechins.
Can green tea help in reducing belly fat?
Yes, studies suggest that the catechins in green tea can help reduce visceral fat, particularly abdominal fat, by improving metabolism and increasing fat oxidation.
Are there any side effects of drinking green tea?
Green tea is safe for most people when consumed in moderate amounts. However, its caffeine content can cause insomnia, anxiety, irritability, upset stomach, or nausea in some individuals, particularly in those sensitive to caffeine.
Can green tea improve skin health?
Yes, the antioxidants in green tea are beneficial for the skin. They help protect against UV rays, improve skin elasticity, and reduce the signs of aging.
Is green tea better than black tea for weight loss?
Green tea typically contains higher concentrations of catechins and antioxidants compared to black tea, which undergoes more processing. This makes green tea potentially more effective at enhancing weight loss.
How does green tea affect people with diabetes?
Green tea has been shown to help regulate blood sugar levels, which can be particularly beneficial for people with diabetes. It helps in moderating insulin levels and reducing blood glucose levels after eating.
Can green tea decrease cholesterol?
Yes, research indicates that green tea can reduce total cholesterol and LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, which are important factors in cardiovascular health.
Does green tea have a role in cancer prevention?
While more research is needed, some studies suggest that the antioxidants in green tea, particularly EGCG, may help in reducing the risk of various types of cancer by protecting cells from DNA damage.